
An email header is the part of an email that contains information about the mail sender, receiver, and subject.
Each email has a custom header that includes technical information for efficient email delivery, and you can view the complete header on email apps like Gmail, Outlook, Yahoo, etc.
In this article, I’ll cover everything you need to know about email headers, including what it is and why it’s essential. I’ll also show you how to view your complete email header across different email apps.
This Article Contains:
(click on the links below to jump to a specific section)
- What Is an Email Header?
- Why Do You Need an Email Header?
- How to Access Your Email Header (Step-by-Step Guide)
- What Are the Different Aspects of an Email Header?
Let’s get started.
What is an Email Header?
The header (internet header) is the section of your mail that includes information like the sender details, receiver details, subject, and date. Other technical details like the Return Path, Reply-To Field, and Message ID are also included in an email header.
Here’s what a complete email header looks like:
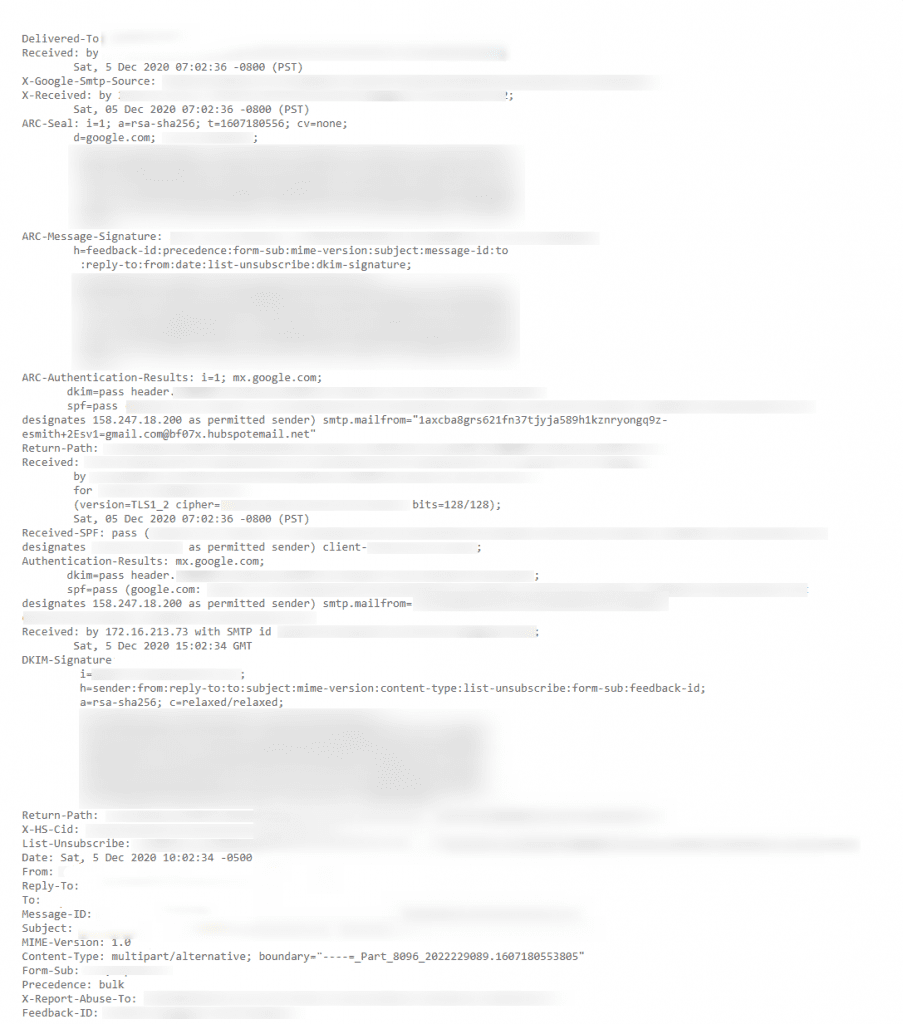
But wait… don’t headers just refer to the top of the email?
In most documents, a header generally refers to the top of the page, while a footer refers to the data at the bottom of the page.
However, email headers don’t function in the same way.
Email headers are specialized pieces of information that contain data that’s vital to mail deliverability. And while some aspects of the email header can be found at the top of your email, your custom header needs to be accessed separately.
So what is the start of the email called?
The information at the start of an email message is called the preheader text.
Your preheader text refers to the lines of text mentioned after your subject line in your inbox. Strong preheader text can go a long way in getting recipients to open your emails.
Now, let’s see why the entire header is important to an email.
Why Do You Need an Email Header?
Here are a few reasons why email headers are essential:
1. Email Headers Protect Against Spam
The header contains several information fields that help email service providers (ESPs) differentiate spam emails from genuine emails. ESPs analyze the header information to determine the legitimacy of the mail and whether it should be delivered to the intended recipient.
These ESP protocols protect your mail account and personal data from phishing attacks and spam emails.
2. The Message Header Clarifies Sender/Receiver Information
Every email header contains the From (message source) and To fields. There’s also the Subject field and Date indicator, highlighting the time and date when a new message was sent.
Without the information from the message header, you wouldn’t be able to view source details or identify the email’s sender or receivers – and you might not be able to determine if the message body (email body) contains legitimate information.
3. Email Headers Help You Track an Email’s Route
When a user sends a new message through email, it originates in a sending mail server and travels through several Mail Transfer Agents (MTAs) before reaching the intended recipient.
When this new message passes through an MTA, it’s automatically “stamped” by the mail server with custom header lines like the recipient, date, and time of the mail.
This header information can help the recipient track the email route — allowing them to check all the MTAs the email passed through to arrive at its destination. This is useful when trying to view message source details and physically track down the origin of malicious and spam emails.
But that’s not all.
If you expand the email header, you can even obtain the IP address of the sender to track the message source further.
How to Access Your Email Header (Step-by-Step Guide)
Here’s a step-by-step look at how you can view a complete email header on email apps like Gmail, Microsoft Outlook and Yahoo Mail:
1. How to View the Full Email Header in Gmail
Here’s how you can view header details in Gmail (Not applicable to the Google apps on mobile devices):
Step 1
Open the Gmail webmail client on a new tab and click on the mail for which you want to see the message header.
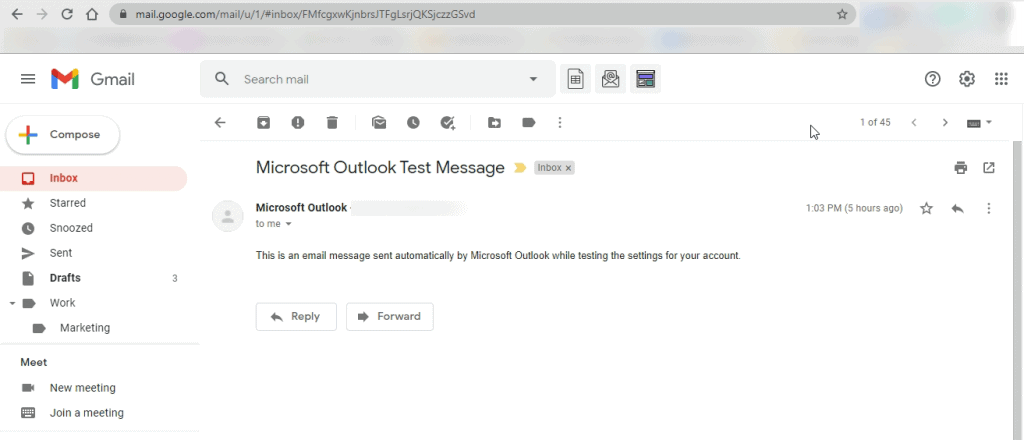
Step 2
When the message body is visible, click on the three dots next to the Reply button to open the menu.
![]()
Then, select Show Original in the drop-down menu.
Step 3
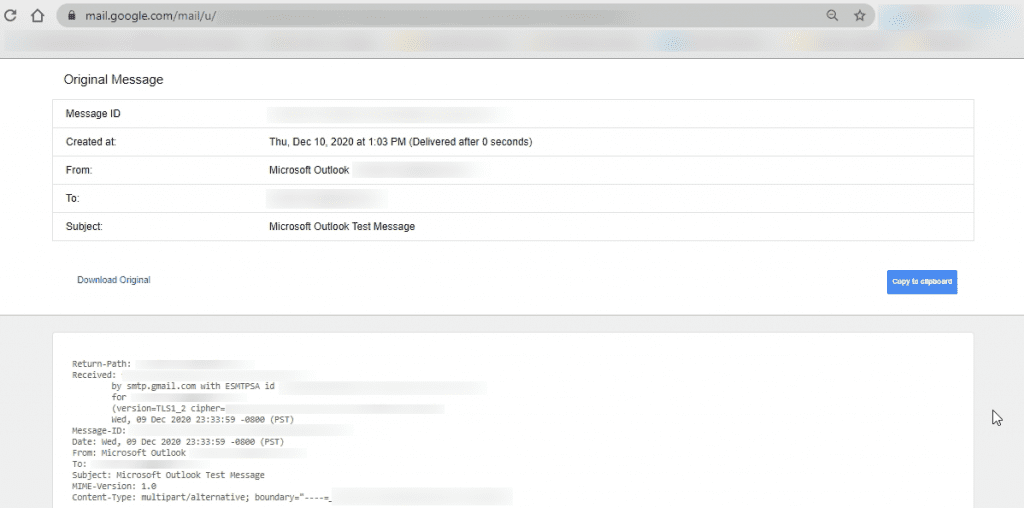
The long header will display in a new window in its original HTML format. It will show some header field details like the IP address, authentication results, DKIM signature, and the MIME-version.
If you want to download and view header details separately, click on Download Original.
2. How to View the Full Email Header in Microsoft Outlook
Here’s how you can view your email header in the Microsoft Outlook email client:
Step 1
Double click and open the mail for which you want to view header details.
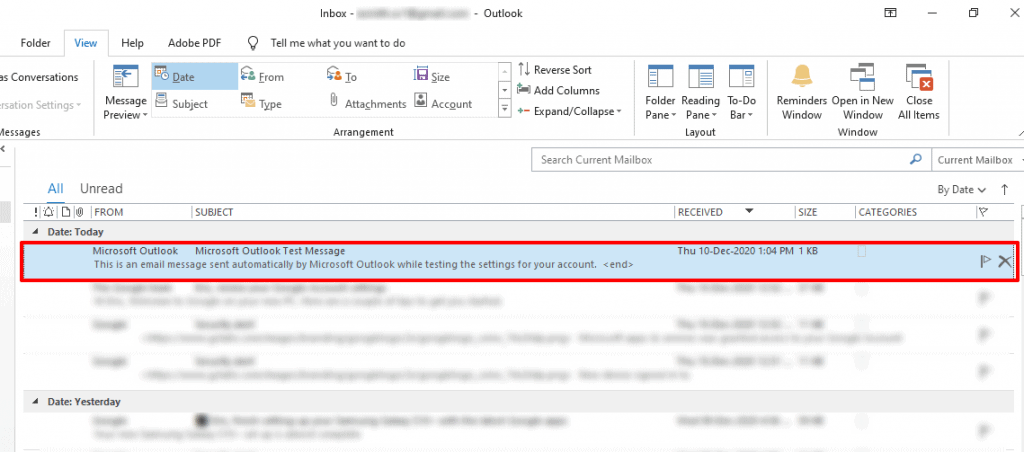
It will open in a new window.
Step 2
Click on File, situated right next to the message tab to open the file menu.
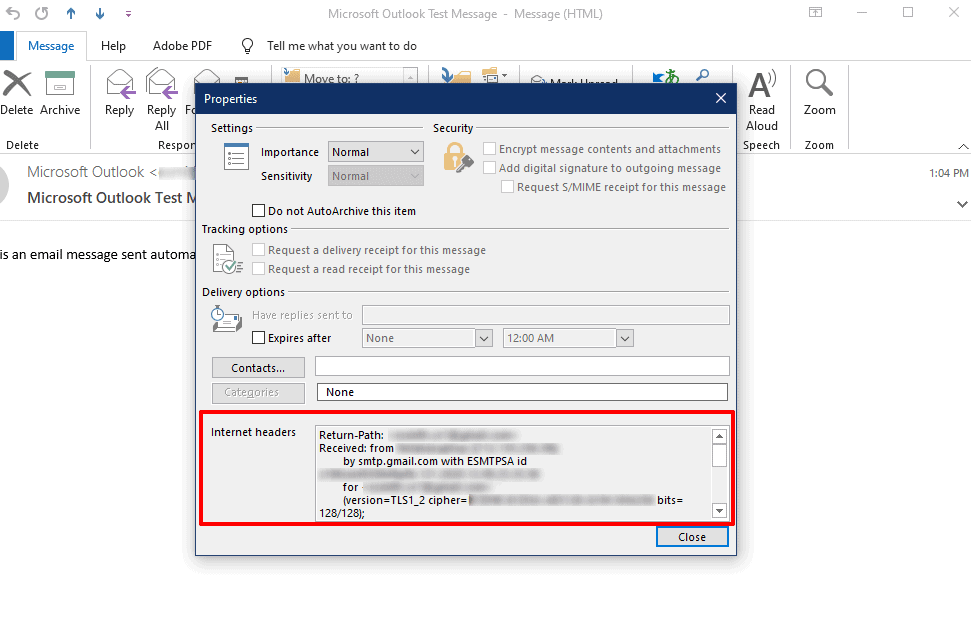
When you can view menu details, click on Properties at the bottom of the window.
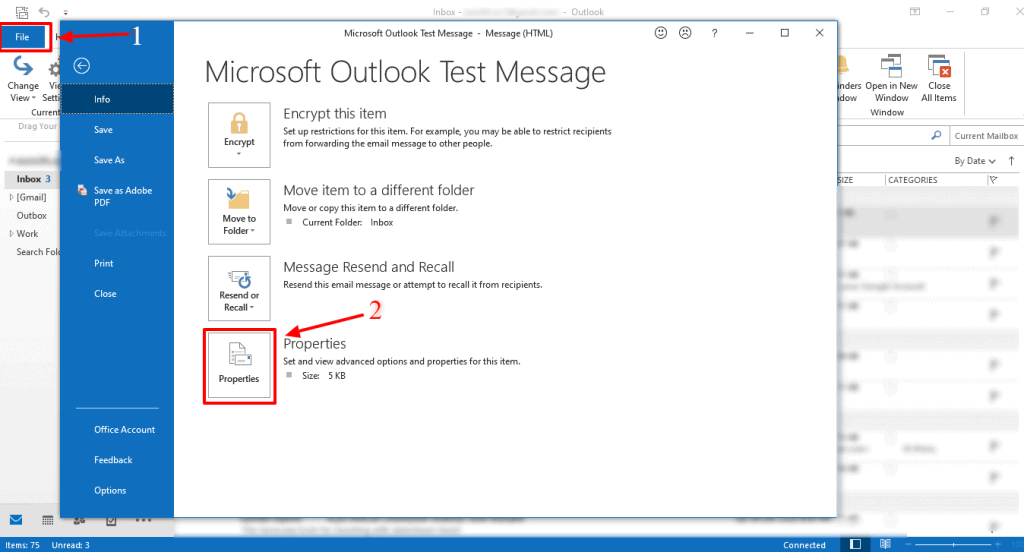
You can find the header information like the IP address of the sender in the Internet headers section of the dialog box.
3. How to View the Full Email Header in Yahoo Mail
Here’s how to view the entire message header in Yahoo Mail:
Step 1
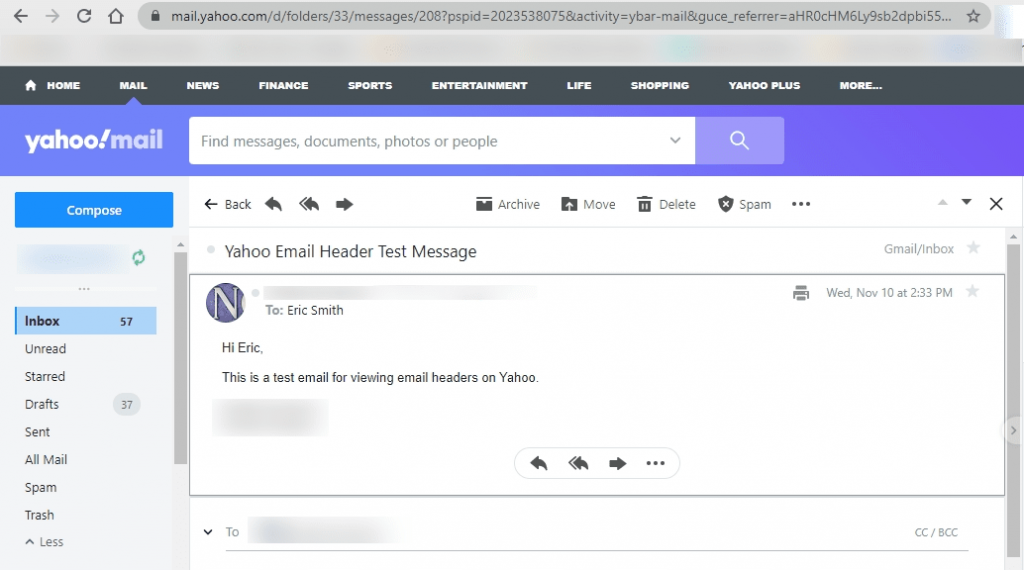
Click and open the email for which you want to see the entire header.
Step 2
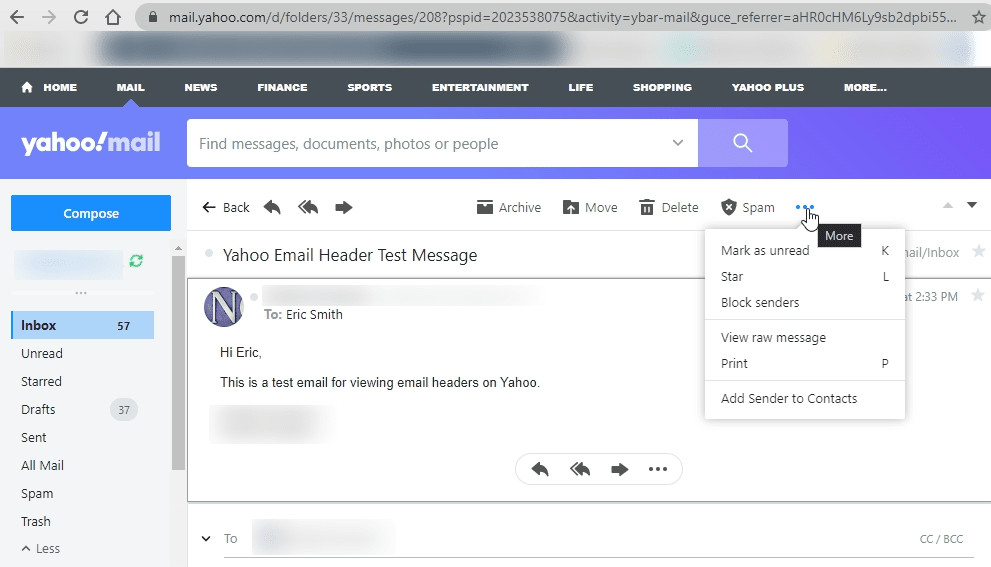
Click on the three dots next to the Spam button on the top right.
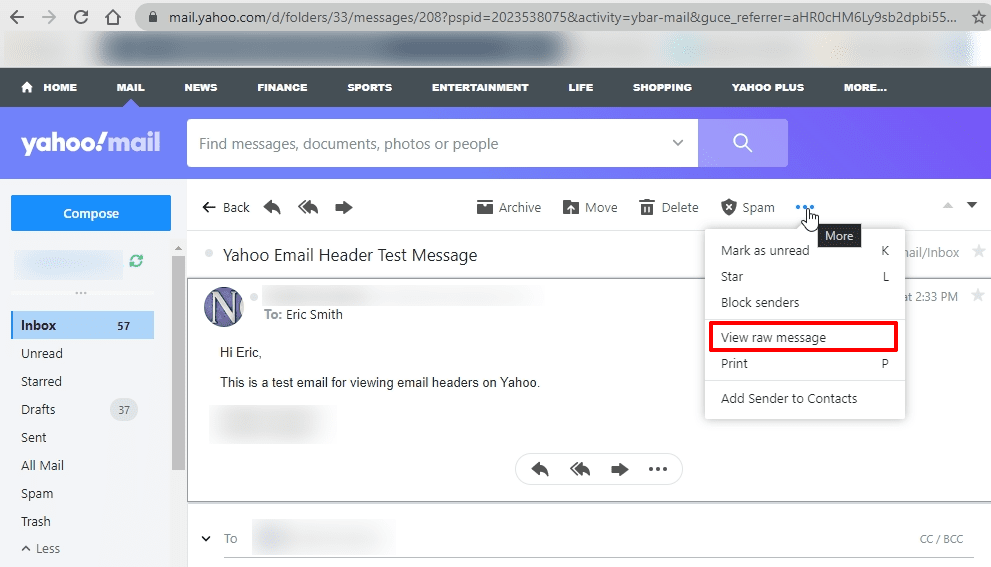
Then click View raw message in the drop-down menu to see the internet header.
The mail header will then open in a new window.
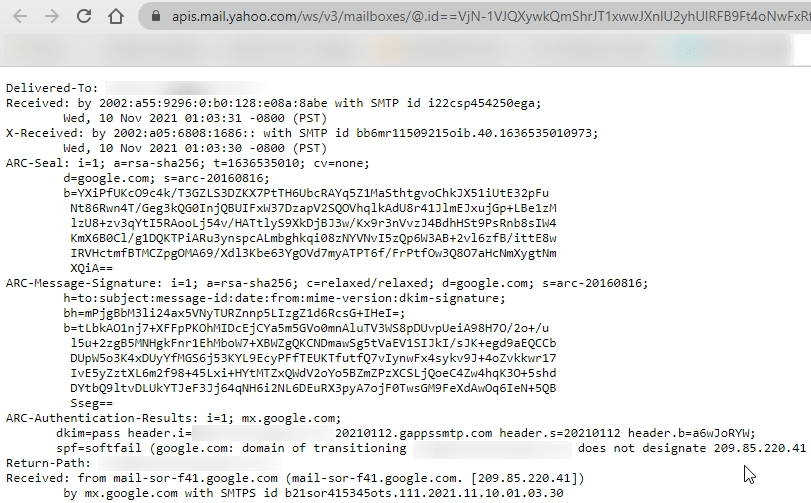
What Are the Different Aspects of an Email Header?
Let’s take a look at the technical aspects of the entire header and what they mean:
- From
- To
- Date
- Subject
- Return-Path
- Domain Key and DKIM Signatures
- Message-ID
- MIME-Version
- Received
- X-Spam Status
And here’s where each aspect is located in an email header:
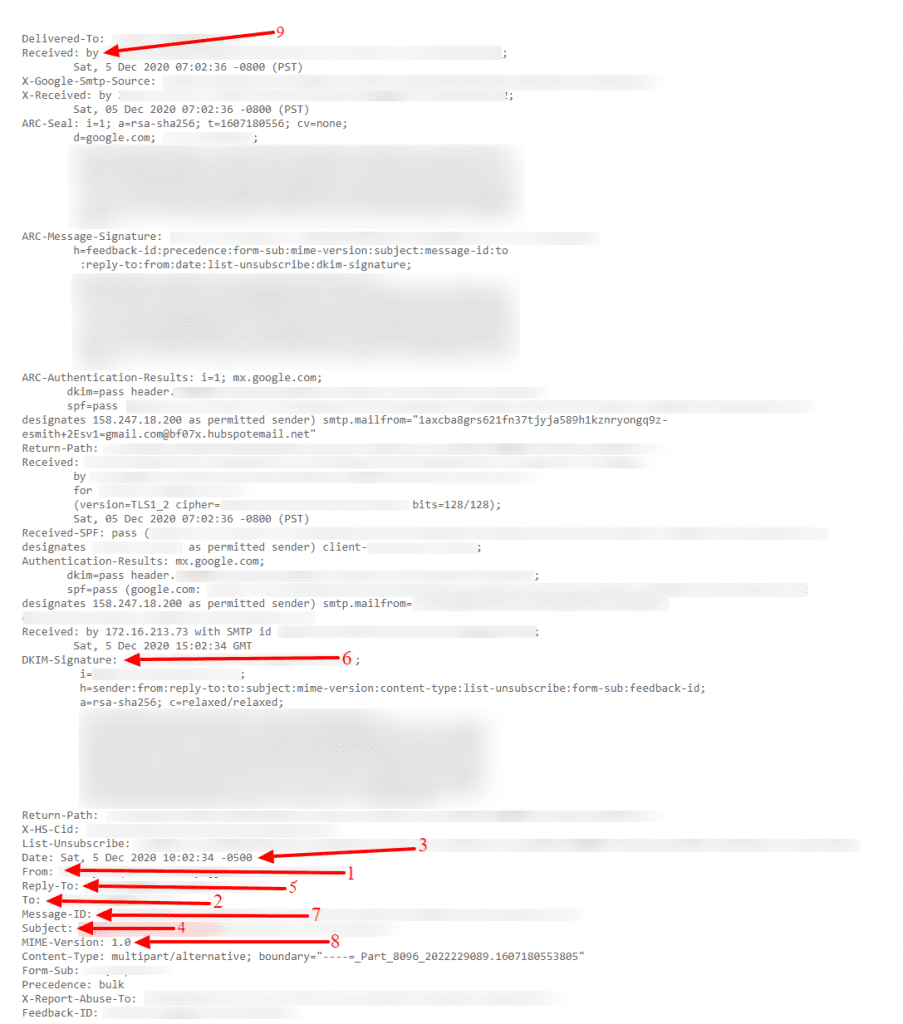
Let’s break each element of the entire message header down:
1. From
The From field of the internet header indicates the name and email address of the sender.
2. To
This field of the mail header contains the email’s receiver’s details.
It includes their name and their mail address. Fields like CC (carbon copy) and BCC (blind carbon copy) also fall under this category as they all include details of your recipients.
If you want to find out more about carbon copy and blind carbon copy, check out how to use CC and BCC.
3. Date
This is the timestamp that shows when the email was sent.
In Gmail, it usually follows the format of “day dd month yyyy hh:mm:ss.”
So if an email had been sent on the 16th of November, 2021, at 4:57:23 PM, it would show as Wed, 16 Nov 2021 16:57:23.
4. Subject
The Subject mentions the topic of the email. It summarizes the content of the entire message body.
5. Return-Path
This mail header field is also known as Reply-To. If you reply to an email, it will go to the address mentioned in the Return-Path field.
6. Domain Key and DKIM Signatures
The Domain Key and Domain Key Identified Mail (DKIM) are email signatures that help email service providers identify and authenticate your emails, similar to SPF signatures.
7. Message-ID
The Message ID header field is a unique combination of letters and numbers that identifies each mail. No two emails will have the same Message ID.
8. MIME-Version
Multipurpose Internet Mail Extensions (MIME) is an internet standard of encoding. It converts non-text content like images, videos, and other attachments into text so they can be attached to an email and sent through SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol).
9. Received
The Received field lists each mail server that an email went through before arriving in the recipient’s inbox. It’s listed in a reverse chronological order — where the mail server on the top is the last server the email message went through, and the bottom is where the email originated.
10. X-Spam Status
The X-Spam Status shows you the spam score of an email message.
First, it’ll highlight if a message is classified as spam.
Then, the spam score of the email is shown, as well as the spam threshold for the email.
An email can either meet the spam threshold of an inbox or exceed it. If it’s too spammy and exceeds the threshold, it will automatically be classified as spam and sent to the spam folder.
Wrapping Up
Email headers play a crucial role in ensuring that your emails are delivered successfully. They’re also key in helping you determine the origin and legitimacy of your emails.
You can check out everything I’ve written in this article to understand why email headers are important and how you can access them on various email clients.
Only GMass packs every email app into one tool — and brings it all into Gmail for you. Better emails. Tons of power. Easy to use.
TRY GMASS FOR FREE
Download Chrome extension - 30 second install!
No credit card required


Loved this. Thanks!!
The spam checker for my email said there should be an unsubscribe link in the header. You don’t mention that here – how, why, when should I put an unsubscribe link in the header? thanks (happy gmass customer, btw)
Hi David,
Unfortunately, at this time, GMass doesn’t have the feature to add an unsubscribe link in your email header. Though we can’t guarantee it, it may be something we can add in our roadmap ahead.
Why isn’t there a way to view an email header when using Hotmail or Gmail on an Android phone? The options just aren’t there.
Awesome post thank you for writing it.
“Return-Path
This mail header field is also known as Reply-To. If you reply to an email, it will go to the address mentioned in the Return-Path field.”
This is not true. They’re two different headers with different purposes. Return path is the address for failure notifications.